INTRODUCTION
The corporate finance field deals with the aspects of funding sources and capital structure of the corporation. Such a field presents actions that managers should take to increase the value of the firm to the shareholders. The present report is based on Vita Life Sciences, a leading Australian-owned pharmaceutical and healthcare unit. It is one of the well-known and established brands throughout Asia and Australia. The brand portfolio of the company is wide which in turn includes g Herbs of Gold, Vita Health, Vita Science, and Vita Life. This report will provide deeper insight into the core activities of VLS and shareholders. The report will also shed light on the key ratios that help in determining the extent to which the monetary position and performance of the company are good. Further, the report also exhibits the share price movement of VLS against the All Ordinaries Index. It will also present whether such business units should be included in the portfolio or not.
Questions
1. Brief Description of the Organisation
Vita Life Sciences Ltd is one of the leading pharmaceutical companies headquartered in Australia and has several branches all over the world. Organisation is engaged in formulating, packaging, and sales and distribution of healthcare products to customers across the globe. It provides vitamins and supplements to consumers in the best possible manner. Vita Life Sciences Ltd has operations in Malaysia, Singapore, Other Asian nations, and its home country Australia as well. In relation to this, revenue has been considerably increased in 2017 as compared to 2016 with a huge margin which shows that the company is making use of resources and as such, generating profits up to a high extent by satisfying customers quite effectually (Vita Life Sciences. 2018). This is evident from the fact that revenue increased up to 6.7 % in the Malaysian market over the previous financial year.
Need to Consult Directly With Our Experts?
Contact UsOn the other hand, revenue declined by 1 % in Singapore in comparison to 2016 figures. The main reason behind this reduction was an increment in advertising and promotional expenditures for maintaining trading in the country in the best possible manner and as such, retail sales were to be effectively maintained. However, in other Asian countries such as Vietnam, Thailand, and Indonesia, revenue increased in the financial year 2017 by 15 % in comparison to previous figures. Major growth in sales and revenue was identified in Vietnam in the 2017 financial year. This implies that Vita Life Sciences Ltd has been successful in its operations quite effectually.
The company's history has been quite impressive and highlights the present picture in effective manner. Vita Health was commenced in Singapore in 1947. Moreover, in 1973, the business opened its own brand of supplements and vitamins. Afterward, revenue was consistently maximised and Herbs of Gold was founded in 1989 thus, healthy foods were being supplied by it (Moreno-Bromberg and Rochet, 2018). In 2001, Vita Life Sciences acquired Herbs of Gold. Moreover, the business has expanded its operations in several nations. The core activities of the organisation are the development and formulation of OTC (Over-the-counter) medicines and the distribution of the same. Moreover, complementary and alternative medications are also formulated and offered for sale to customers. Another core activity of business is to provide dietary supplements and health-related foods are also sold under varied brand names in various nations. Thus, quality-assured products are made to enhance customer satisfaction.
2. Ownership-Governance Structure of Company
The main shareholders of Vita Life Sciences Ltd are Mr Vanda R Gould and Mr Shane Teoh. They are the directors of the company with more than 20 % of shareholdings in the shares of organisation. In this aspect, Mr. Vanda R Gould has 51.30 % and Mr Shane Teoh has nearly 42.44 % of the shareholding in the company. It can be said that both of these directors have a substantial part of shares in their holdings. On the other hand, other directors are Mr Andrew O'Keefe, Mr. Jonathan J Tooth, and Mr Henry G. Townsing. It clearly highlights that Mr Vanda R Gould and Mr Shane Teoh both have major shareholdings in the company. Furthermore, it also shows that the firm is a non-family company as no members have similar surnames in the organisation. This is evident from the fact that a firm's governance is managed by different personnel (Rocheteau, Wright, and Zhang, 2018).
The main people involved in the company's governance are the CEO (Chief Executive Officer of Australia is Mr Andrew O'Keefe. The chairman of the company is Mr Henry G Townsing. On the other hand, Board members are Chin L Khoo who is Company Secretary and CFO (Chief Financial Officer). Mr Shane Teoh is a Non-executive director Mr. Vanda R Gould is also a Non-executive director and Mr Jonathan J Tooth is in the same post as well. Mr Henry G Townsing having more than 5 % of shareholding is present in corporate governance and other directors such as Vanda R Gould and Mr Shane Teoh are also engaged in the firm's governance. Thus, it can be stated that Vita Life Sciences Ltd is classified as a non-family company involving no family members in the ownership-governance structure.
3. Computation of Financial Ratios
- Financial ratios of the past four years starting from 2014 to 2017
|
Particulars |
Formula |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
|
Return on Assets |
(NPAT / Total Assets) |
27.85 |
14.02 |
10.33 |
8.77 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Return on Equity |
(Net Profit After Tax / Ordinary Equity) |
38.67 |
19.83 |
14.55 |
11.96 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Debt Ratio |
Total Liabilities / Total Assets |
0.3 |
0.31 |
0.28 |
0.24 |
- Explain the phenomenon of Total assets and Owner's Equity
The Total Assets (TA) and Owner's Equity (OE) are the relationship of organisation's total assets to that of part-owned by shareholders of the company. The phenomenon captured by TA/ OE variable is that it shows how effectively the firm is utilising total assets to generate sales and giving out the return on owners' equity in the form of dividends by producing desired profits in the best possible manner. This is essential for businesses to earn profits in order to enrich shareholders and maximise their wealth with much ease. It is required so that more investment may be garnered by the company quite effectually (Mulherin, Netter, and Poulsen, 2018). The investor is planning to invest in the company an amount of 10 million to generate returns.
Return on Assets and Return on Owners Equity is quite useful for organisation in order to ascertain profitability position in the best possible manner. Vita Life Sciences Ltd has had overall good revenue in the past four years. However, ROA has declined in recent years. This is evident from the fact that ROA in 2014 was 27.85 % which was reduced to 14.03 % in the next year. On the other hand, the ratio in 2016 was further minimised to 10.33 %. While, in 2017, it was 8.77 %. This means that the company's ROA is considerably decreased from 2014 to 2017. This implies that the firm is unable to effectively utilise its assets to generate sales and as such, it is declined in subsequent years.
On the other hand, ROE means how effectively a company uses its shareholders' investment to produce net income in the best possible way (Dang, Li, and Yang, 2018). The ratio was 38.67 % in 2014, while in next year was 19.83 % which significantly declined. Furthermore, ROE was 14.55 % in 2016 and 11.96 % in the 2017 financial year. This clearly shows that Vita Life Sciences Ltd is not effectively utilising shareholders' money in optimised manner. ROA and ROE are integral parts of the company as they lead to effectively ascertaining true profitability position. In relation to this, organisation has adequate revenue but ROA and ROE are not good which implies that these two ratios computed highlight inefficiency of the company in generating sales with regard to assets and shareholder investment. It is impacting the firm's profitability adversely.
- Discussing why ROE is greater than ROA
ROE and ROA of the organisation have however decreased in recent years. In this aspect, the firm has a low ROA in comparison to ROE that highlights the company's debt is increasing (Mizen, Packer, Remolona, and Tsoukas, 2018). This is not good for Vita Life Sciences Ltd as it leads to an increase in loan repayment installments to creditors. Furthermore, the solvency position of the company is also impacted adversely. Moreover, higher debts led to a decrease in ROA which is an adverse situation for the company.
4. Preparation of Graph in Monthly Share Price of the Organisation
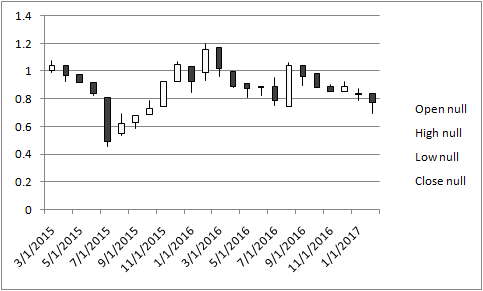
The above graph represents the monthly price of shares over the last two years of the company. It shows that the company's performance over the last two years is not good. This is evident from the fact that organisation's shares are gone down. Furthermore, the value of beta is 0.81 which means that the investor has moderate risk while investing in the company. Beta shows that the firm has moderate volatility and as such, investors can expect a return in the long run. Moreover, organisation is required to utilise assets and shareholders' investments to increase profitability aspect in effective manner.
5. Factors Influencing Shares Price of Company
- Impact of competitors-
The competitors' strategies affect the market price of shares quite adversely. This shows that with well-structured strategies implemented by the rivals, prices are affected. It is also evident from the fact that Vita Life Sciences Ltd's share prices are affected by strategies implemented by competitors (Hansen, 2018).
- Macroeconomic factors-
This is another factor that affects price shares. Macroeconomic factors such as inflation rate, exchange rate, and supply of money lead to a decrease in the market price of shares.
- Changes in analysts forecast-
It is another factor affecting the share price of Vita Life Sciences Ltd quite adversely. If analysts are changed frequently, then forecasts may be affected as no two analysts have the same forecast principles (Armour and Enriques, 2018).
- Unusual write-offs-
Unusual write-offs also led to changes in the share prices of the company. If the amount from debtors is a write-off in the year and is received afterward influences shares of organisation.
- Management changes-
Management is an important part of the company as when frequent changes occur in organisation's management team, the prices of shares are affected.
6.
1. Beta Value of the Company
From assessment, it has been identified that the beta value of Vita Life Sciences accounts for .81 respectively. Referring to beta value, it can be depicted that the stock or shares of the company are volatile in nature to some extent (Vita Life Sciences Ltd, 2018). Moreover, a beta of securities with less than 1 is considered as less volatile in comparison to the market from a theoretical perspective.
2. Assessing the Required Rate of Return
Computation of required rate of return
|
Particulars |
Figures |
|
Beta value |
.81 |
|
Risk-free rate (Rf) |
4% |
|
Market risk premium (Rm -Rf) |
6% |
|
Expected market return (Rm) |
10% |
|
Required rate of return Rf + beta (Rm - Rf) |
8.86% |
On the basis of the CAPM model, against the risk undertaken shareholders are expecting an 8.9% return from the stocks of VLS.
3. Stating Whether the Company Chosen for the Investment Purpose Comes Under the Category of Conservative
Conservative investment implies the one where the investor lays a high level of emphasis on investing money in lower-risk securities such as fixed income and business units with large capitalization (Häusermann, 2018). Hence, referring to beta value (.81) and market capitalization ($42.78 million) it can be presented that chosen company does not fall into the category of conservative investment. Moreover, in this, the beta value is higher such as .81 significantly, and the market capitalization of the company is considered as lower. Thus, all such aspects clearly present that the company selected for the investment purpose such as VLS is not a conservative investment.
7.
1. Assessing WACC for VLS
Weighted average cost of capital
|
Particulars |
Figures |
|
Share Price |
0.78 |
|
Shares O/S |
56,717,026 |
|
|
|
|
Market Cap (E) |
44239280.28 |
|
|
|
|
Stock Beta |
0.81 |
|
Risk-Free Rate |
0.04 |
|
(e.g. return on 10-year treasury bonds) |
|
|
Required Market Return |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
Market Risk Premium |
0.06 |
|
|
|
|
Cost of Equity |
8.9% |
|
Particulars |
Figures |
Weights |
|
Equity |
44239280.28 |
0.96 |
|
Debt |
1987000 |
0.04 |
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
46226280 |
1 |
|
Particulars |
Figures |
|
Interest rate |
5% (Interest rates in Australia, 2018) |
|
Tax rate |
30% (Company tax rates, 2018) |
Boost Your Grades with Online Exam Help
WACC = ke * weight of equity + interest rate * weight of debt (1 - tax rate) (García, 2017)
WACC = 0.089 * .96 + 0.05 * .04 (1 - .30)
= 0.085 + 0.05 * 0.028
= 0.085 + 0.0014
= 0.0868 or 8.7%
2. Explaining the Implications of High WACC on Management's Evaluation Pertaining to the Prospective Investment Projects
By doing the assessment, it has been found that a high WACC has a greater impact on the evaluation of prospective investment projects. The level of WACC decreases when firms resort to debt sources rather than equities. High WACC presents that greater risk is associated with the firm's operations. Hence, in the case of investment projects, high WACC shows a lower level of return with the investment project and thereby affects the decision.

Stuck with your Assignment?
Hire our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS and Get 100% Original Document on any Topic to Secure A+ Grade
Get Assignment Help
8.
1. Analyzing the Debt Ratio of Vita Life Sciences in Relation to the Past Two Years
Debt-equity ratio: This measure presents the manner in which a business entity has fulfilled its monetary requirements through either debt or equity or both. In other words, the debt-equity ratio presents how much loan is undertaken and shares are issues for financing business projects.
The computation of debt-equity ratio for the accounting years 2016 and 2017 are as follows:
|
Particulars |
2016 |
2017 |
|
Long-term debt |
2 |
2 |
|
Shareholders' equity |
23 |
25 |
|
Debt-equity ratio |
0.09 |
0.08 |
The above-depicted table shows that, in the accounting years 2016 and 2017, the debt-equity ratio of VLS accounted for 0.09 & 0.08 respectively. Hence, a decreasing trend has been assessed in the debt-equity measure of VLS over the time frame. Considering the current results or outcomes it can be depicted that the debt-equity position of VLS was not good in the period of 2016 & 2017. On the basis of standards, the solvency position of the company can said to be effectual when the debt-equity ratio is equal to or in line with .5:1. Currently, the capital structure of the company does not appear stable. The rationale behind this, the business unit has fulfilled most of its financial needs or requirements through equity shares rather than debt. Thus, for developing optimal capital structure VLS should make focus on the following .5:1 ratio. On the basis of this, VLS should take resort to 1 debt against 2 equity shares.
2. Stating the Adjustment Which Vita Life Sciences Have Done Regarding Gearing Ratio
In the context of the gearing ratio, it has been found from the annual report that approximately 191204 shares were bought back for the accounting year ended on 31st December 2017. This is one of the main causes behind the increase in shareholders' equity and the declining trend in the debt-equity ratio (Annual report of VLS, 2018).
9. Discussing Dividend Policy Which is Implementing by Vita Life Sciences
The annual report of the VLS presents that the financial performance of the company for the year ended in December 2017 was good. Hence, by taking into account financial performance business unit has declared 2.25 cents as a dividend per share. By doing research, it has been identified that from the period of 2014 to 2017 company is offering similar dividends to the shareholders. Hence, by taking into account the overall evaluation it can be presented that a stable or constant dividend policy is followed by VLS. The company undertakes and implements such dividend policy with the motive to maintain the faith of shareholders in the company's operations.
10. Giving Recommendation to the Client Whether Such a Company Needs to be Included in the Investment Portfolio or Not
|
To The Client Date: 23rd April 2018
Subject: Investment decision and evaluation
This is to inform you that VLS is one of the leading and well-known brands in the pharmaceutical sector. Ratio analysis has been conducted to analyze or evaluate the profitability aspect of the business unit. Hence, from ratio analysis, it has been found that the profitability position of VLS has decreased over the time frame. In comparison to the prior years, the ROA and ROE of VLS at the end of the accounting year 2017 accounted for 8.77% & 11.96% respectively. The decreasing trend of the ratio shows that in the accounting year 2017 business unit failed to make effectual use of assets and investments made by the shareholders. It is reported to the client that the debt-equity position of VLS was not good in the year of 2016. Currently, the business unit is following a regular and constant dividend policy. Investment in the securities of VLS is not considered conservative. Moreover, beta value is within the range of .75-41 which in turn shows a moderate risk level. Besides this, WACC pertaining to VLS implies 8.7% significantly which is neither too high nor too low. Hence, if the client prefers investing money in securities with high and moderate risk levels then it might offer high returns in the long run. In accordance with the value investing approaches, investments should be made in securities with a high PE ratio>10, profitability, and solvency position. In the context of VLS, the profitability and solvency position of the company was not good. In addition to this, due to high beta and low market capitalization value investment in the shares of VLS is not considered as conservative. Thus, investors should avoid making investment in the shares or stocks of VLS. Hence, the client should not include VLS security in his/her portfolio.
From Financial analysts |
Boost Grades with Cheap Assignment Help Now
CONCLUSION
By summing up this report, it has been concluded that VLS has built and maintained a wide product portfolio. The company is focusing on providing customers with high-quality pharmaceutical products or services. Besides this, it can be seen in the report that the profitability level of the company decreased over the time period. Further, it has been articulated that the capital structure maintained by VLS is not optimal. It can be summarized from the report that the weighted average cost of capital pertaining to VLS implies 8.6% significantly. In addition to this, it can be depicted from the evaluation that VLS is offering dividends to the shareholders regularly or each year. However, such a business unit will prove to be fruitful for investment purposes only in the long run. If an investor wishes to earn a fixed or suitable return by investing money in lower risky securities then VLS stocks should not be included in the portfolio.
REFERENCES
- Armour, J. and Enriques, L., 2018. The Promise and Perils of Crowdfunding: Between Corporate Finance and Consumer Contracts. The Modern Law Review. 81(1). pp.51-84.
- Dang, C., Li, Z. F. and Yang, C., 2018. Measuring firm size in empirical corporate finance. Journal of Banking & Finance. 86. pp.159-176.
- García, F. J. P., 2017. The WACC. In Financial Risk Management (pp. 345-351). Palgrave Macmillan, Cham.
- Hansen, C. B., 2018. Peter Birch Sørensen University of Copenhagen:" Taxation and the optimal constraint on corporate debt finance: Why a comprehensive business income tax is suboptimal". Virtual Reality.
- Häusermann, S., 2018. The multidimensional politics of social investment in conservative welfare regimes: family policy reform between social transfers and social investment. Journal of European Public Policy. 25(6). pp.862-877.
- Lee, H. and Park, K., 2018. Advances in the corporate finance literature: a survey of recent studies on Korea. Managerial Finance. 44(1). pp.5-25.
- Mizen, P., Packer, F., Remolona, E. and Tsoukas, S., 2018.Original sin in corporate finance: New evidence from Asian bond issuers in onshore and offshore markets (No. 2018/04).
- Moreno-Bromberg, S. and Rochet, J. C., 2018. Continuous-Time Models in Corporate Finance, Banking, and Insurance: A User's Guide. Princeton University Press.
- Mulherin, J. H., Netter, J. M. and Poulsen, A. B., 2018. Observations on research and publishing from nineteen years as editors of the Journal of Corporate Finance. Journal of Corporate Finance.
- Rocheteau, G., Wright, R. and Zhang, C., 2018. Corporate finance and monetary policy. American Economic Review.108(4-5). pp.1147-86.



 Company
Company


















