INTRODUCTION:
It is very difficult to understand human behavior. This is because human being changes their behavior according to the situation. Human behavior is the response of an individual to internal or external stimuli (Hillson and Murray-Webster, 2017). The behavior of humans is influenced by several factors such as culture, values, and beliefs. Besides this, personality and traits are also an important element in this. There are various mysteries involved in understanding human behavior. This report will throw light on several theories that are given by scholars and psychiatrists. Also, it will reflect on evaluating theories on the basis of the human aspect.

John Bowlby
He gave theory related to children. The theory was based on the attachment of children to their parents. In this theory, he observed that children experience distress when they are separated from their mothers. Also, it showed that attachment can be characterized according to the behavior of children (Daly and Wilson, 2017) A child is always connected to her mother in social, emotional, and cognitive ways. This creates a link between them. He further developed stages of development.
- Pre-attachment- in this infants act in such a way that attracts adults such as crying, smiling, etc. (John Bowlby,2018).
- Attachment in making began to develop a sense of trust in their mothers.
- Clear cut attachment- In this stage attachment is established. Infant prefers to be with their mothers than anyone else.
- Formation of reciprocal relationship- The infant understands about situation. A sense of security is developed in them when their mother is not around.
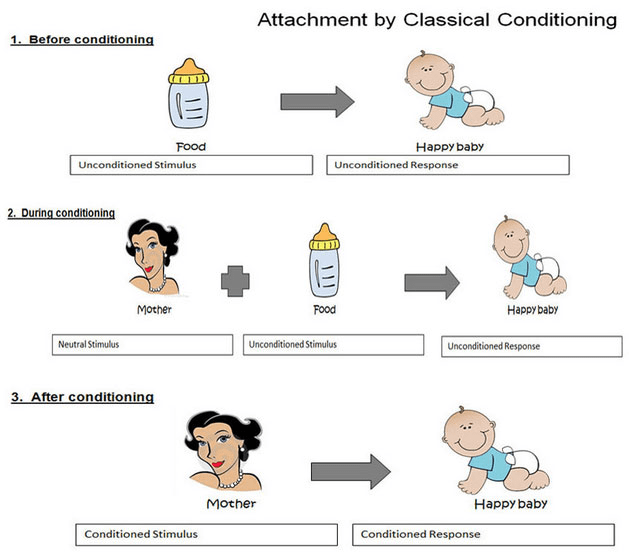
Attachment theory - it was developed by Bowlby. In this, he suggested that attachment is a set of learned behaviors. But the base for this is food. Children will always get attached first to the person who will feed them. Usually, it includes the mother that feeds the child. Then, infants learn to associate with their mothers (Blake, McAuliffe, and Wrangham, 2015) This will begin the process of classical conditioning. In addition to this, there are certain changes that occurs in behavior such as crying, smiling, etc. It brings responses from others. Thus, by going through the process of operant conditioning infants learn to repeat those behaviors. Besides this, there are three attachment styles that are secure, anxious avoidant insecure, and anxious resistant insecure. This shows how attachment is formed at different levels.
On the other hand, another theory of attachment states that children come into this world to form attachments. They are already prepared for this. Infants build social relations to develop behaviors such as crying and smiling. So it is concluded that attachment is developed by care, not by food. Bowlby also stated that children only form one attachment and that helps in explore the world and survive (Rodríguez and Calvo-Flores, 2014) This one attachment acts as a prototype for all social relationships in the future. So if this attachment is disrupted it can lead to major consequences. At last, it shows that there is a specific period for forming this attachment which is 0-5 years. The child may have reduced intelligence if attachment is not developed in this period.
Mary Ainsworth- Strange situation
Mary Ainsworth designed a structure to measure the quality of attachment. In this 8 stages were included that described a relationship between mother and child (Mary Ainsworth, 2016) The 8 stages are given below:-
- Stage 1 - Mother and child enter the playroom
- Stage 2 - The child is encouraged to explore
- Stage 3 - Stranger enters and attempts to interact
- Stage 4 - Mother leaves while the stranger is present
- Stage 5 - Mother enters and the stranger leaves
- Stage 6 - Mothers leaves
- Stage 7 - Stranger returns
- Stage 8 - Mother returns and interacts with the child
From the above, it was found that there are three attachment styles. These are secure, insecure avoidant, and insecure ambivalent. These styles description is as follows:-
Secure attachment- In this children are full of confidence and highly attached to their mothers. This helps in fulfilling their needs (Koelsch, Jacobs, and Gebauer, 2015) In this infants develop a strong attachment when their needs are fulfilled.
Insecure avoidant - in this children are independent both physically and emotionally. They do not seek to have contact with attachment figures when distressed. These types of children are very insensitive and their needs are rejected by parents. Due to this they highly get emotionally distressed.
Insecure resistant - Here, the child develops an uncertain behavior towards the attachment. This is because of the surroundings. When they are in distress they are not comfortable interacting. This behavior results in an inconsistent level of response to their needs.
This is concluded from strange situations that child attachment will depend on how their mothers react or behave with them (Almeida, Rossetti, and Coelho, 2017) Also, it depends on the mother's behavior. There are two points in this:-
- First sensitive mother will respond in smooth way. They are more likely to have a very close attachment to children. There will be a secure attachment between them. The child will develop positive thinking and will be helpful to others.
- On the contrary, mothers who are less sensitive will respond in negative way. Their child will be impatient. There will be an insecure attachment between them. In this, there will be a risk of social or emotional behavioral problems.
Dollard And Miller
They both developed theories related to the personality of humans. It was based on Clark L. Hull's learning theory (Gwynne and Hulse, 2017) They showed the learning process by using an S- R model of mental processes. According to Dollard and Miller, human behavior occurs in cues. A cue may be any stimuli.
- Response hierarchy and learning - It means change in response due to learning. In this learning occurs in four ways that are drive, cue, response, and reinforcement. A drive may be a stimulus such as hunger. If drive is reduced reinforcement will occur. Reinforcement is the connection between cue and response (Dollard and Miller,2018). It concludes that drive will force people to learn. The cue must lead to getting some reward as reinforcement.
- Role of drives - There are some primary drives such as hunger, thirst, etc. that are inborn. They occur naturally and force us to learn. For example- a person may feel hungry when he sees his favorite food even if he has already eaten (Safa and Herawan, 2015) These drives are known as secondary drives. Another example is pain. It encourages a person to act, thus any response that will reduce this will be reinforced.
- Cue responses- A cue may result in the occurrence of a new cue. It means that what one learns in a situation will occur in a similar situation. It is known as stimulus generalization.
- The social role of learning - In this miller and Dollard showed how to understand human behavior. For this, they must know the process of learning. This will help in finding out the social conditions under which learning was gained (Grossmann, Brienza, and Bobocel, 2017). Also, human learning can vary from social to interpersonal context. One example is limitation. It means copying other behaviors.
- Psychoanalytic approach to neurosis- In this S r model was applied. It showed how neurosis is characterized into three categories that are misery, stupidity, and symptoms. Misery is related to conflicts. Stupidity refers to the fact that conflicts that result in misery are unconscious. The last symptoms are phobias, hysteria, etc. that arise when one is in a state of conflict-produced misery. This creates a feeling of fear among them.
- Therapeutic techniques - In S R this technique leads to new learning. This is because in order to solve conflict new learning is required (Daly and Wilson, 2017). Therefore, one technique that is available for this is psychoanalysis. In this associations directly instruct patients to their consciousness. Another technique that is available is transference. In this patients express their feelings to the therapist.
- Behavioral approach - thus, it is concluded from S R theory that mental process arises by associating cues and responses.
Get dissertation help from our experts!
CONCLUSION :
From this report, it is concluded that the behavior of humans depends on the situation. It changes from time to time. The behavior of humans is influenced by several factors such as culture, values, and beliefs. Human behavior is affected by several factors. This brings a change in their mental health. Also, it is said that a child is always connected to her mother in a social, emotional, and cognitive way. This is concluded from a strange situation that child attachment will depend on how their mothers react or behave with them. Also, it depends on the mother's behavior. Hence, it is the behavior of a child who will mostly be dependent on his mother. At last, it is concluded that it is very difficult to understand human behavior.
You may also like: Identifying Health And Diseases In Communities
REFERENCES :
- Almeida, J.E., Rossetti, R.J., and Coelho, A.L., 2017. Serious games for the human behavior analysis in emergency evacuation scenarios. Cluster Computing, 20(1), pp.707-720.
- Blake, P.R., McAuliffe, K., and Wrangham, R., 2015. The ontogeny of fairness in seven societies. Nature, 528(7581), p.258.
- Daly, M. and Wilson, M., 2017. Homicide: Foundations of human behavior. Routledge.
- Grossmann, I., Brienza, J.P. and Bobocel, D.R., 2017. Wise deliberation sustains cooperation. Nature Human Behaviour, 1(3), p.0061.
- Gwynne, S.M.V., and Hulse, L.M., 2017. Modeling and influencing human behavior in fire. Fire and Materials, 41(5), pp.412-430.
- Hillson, D. and Murray-Webster, R., 2017. Understanding and managing risk attitude. Routledge.
- Koelsch, S., Jacobs, A.M., and Gebauer, G., 2015. The quartet theory of human emotions: an integrative and neurofunctional model. Physics of Life reviews, 13, pp.1-27.
- Rodríguez, N.D., and Calvo-Flores, M.D., 2014. A fuzzy ontology for semantic modeling and recognition of human behavior. Knowledge-Based Systems, 66, pp.46-60.
- Safa, N.S., and Herawan, T., 2015. Information security conscious care behavior formation in organizations. Computers & Security, 53, pp.65-78.


 Company
Company













